Preserving Pristine Wetlands
An Ecosystem-based, in-situ impact factor considerate approach to save livelihood of residents and life of a Wetland.
I guess we all are aware of the various geopolitical events as conventions, meetings, and conferences happening in the domain of Climate Change at regular intervals. The world has come together and formed various scientific and geopolitical forums to negotiate about actions to be taken for adaptations to climate change and mitigating the same. One of the key moments in this global pursuit has been the setting up of the Green Climate Fund (GCF), in which the richest countries on the globe have set up the fund to help poor countries in adaptations to climate change. Apart from these, various private entities too, are foraying into the arena of climate financing and climate investments.
Problem Statement:
Although the world has started to act lately by setting up funds and programs like GCFs. One critical thing remains that these funds and programs remain centralized and are allotted for taking certain actions anywhere in a manner, that is put forward in the top-to-bottom model of interventions. It is one package for all scenarios, and many times interventions as these fail to solve a crisis at a given place and also introduce new problems and conflicts there. Sometimes allotted heavily for an ecosystem, which may require lesser interventions, and after allotment action taken causes more harm than the previous state. All these issues lie due to the central nature of this fund, which provides incentives for a locality or unit to apply for these funds. We must realize that nature is a heterogeneous system and any homogeneous approach implied not only a maybe futile attempt but also can cascade the problems further. In wake of such issues, we have taken a task to build a model to determine the nature and amount of intervention required by an ecosystem to maintain its sustainability with minimal side impacts and conflicts. For this purpose we have chosen one of the largest wetlands in India, which is full of enormous constraints; some of them like residents making their lives on a meager 1.33 USD/day average, they have a single window for cultivation in a year which must feed them throughout the year. In such extreme constraints, people are compelled to harm the ecosystem more to get more resources. We believe a model developed in a highly constrained environment like these will work everywhere with little study of those sites and modifications.
Title:
“Equitable and customized allotment of climate funds in the wake of COVID-19 pandemic based on in-situ impact factors. “
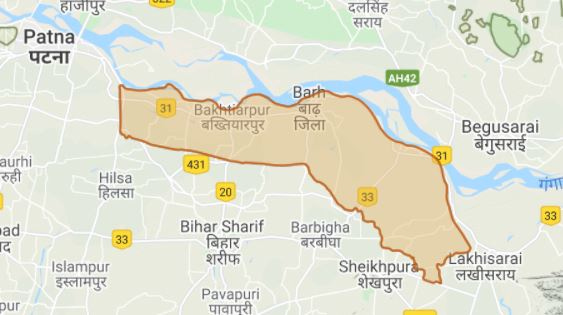
Study Site:
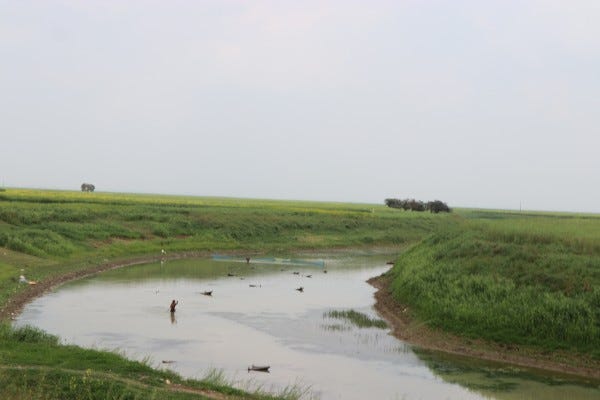
Location: Mokama Taal, Bihar, India
Country: India
Co-ordinates: 25.362333° N, 85.915772° E
25.340878° N, 85.989439° E
25.270647° N, 85.993011° E
25.244103° N, 85.907633° E
25.279869° N, 85.853850° E
Rationale behind Study Site:
Mokama Taal, a large perennial wetland, around 178 square-kilometers in size, lies in jurisdiction of three districts namely Patna, Begusarai, and Samastipur. It is a unique ecosystem serving not only larger cause of contribution to the regulation the climate in North and South Bihar region, but also serves livelihood and lives of at least half million people inhabiting this wetland in the form of villages scattered like islands across whole of wetlands.
It is fragile ecosystems driven entirely by annual water cycle, and with the impacts of climate change, as cited in many research journals about rising frequency of extreme weather events and irregular weather patterns, the natural water cycle through out the year is changing in this region. It is evident from many hydrological journals as well as from the conversation with local inhabitant there. So, it is quite evident that people this area will be hit worst by impacts of climate change.
Secondly, with low income groups residing there pose challenges of monumental scale for researchers to create balance between the nature and people living there by finding a way for external intervention, yet locally negotiable, acceptable, and suggested.
This research area is ideal one for the task of research in the field of mitigation of climate change and adaptation to it. Any model drafted in such a constrained and challenging environment with very limited resource could easily be customized and modified for other less constrained regions easily and could be streamlined at faster pace. The impact of COVID-19 makes it more challenging and constrained.
A Tentative methods to be employed:
There are 72 island type villages located in study area. We have devised two phase survey and data collection mechanisms for entire are. First phase is preliminary one, to mark boundary for each village on map and type and identify all the possible parameters needed to be studied in the field. Timeline for preliminary phase is kept between 36 to 48 days, for a quick survey visiting the whole area.
Secondary phase is heart of the entire work is more extensive and exhaustive one. In this, there is provision of collection of all the survey scientific as well as socio-economic required for the research. For data collection, We have determined four categories as;
1.) Interviews, conversation based for various age groups (16-20, 21-30, 31-40, 41-50, 51-60, 61-70) gender-wise.
2.) Culture, tradition, and religious practice-based data from the field.
3.) Scientific data of past 40-50 years, i.e., satellite imagery, rainfall, floods, weather and hydrological.
4.) Socio-economic data as agricultural output, population, household income, education, income.
Steps for data collection, processing, storage and usage:
1. Categorization of all villages into clusters of 3 or 4 villages. Categorization is done on following parameters in priority order.
a. Distance: - The nearby villages with minimum distances among them respectively are categorized on priority basis. This helps in scheduling the field visits with maximum coverage and lesser travel costs. This also saves a lot of time in field visits.
b. Connecting Water bodies: - Villages on the edge of the same riverine or water bodies are categorized on next priority basis. As this provides similar ecosystem accessed by different villages. It helps in identifying the drivers of change as different villages might have little different agricultural practice based on community and customs. This classification is important to study, how similar ecosystems faces different stresses on the basis of various socio-economic factors.
c. Agricultural or Other socio-economic practices: - This categorization is based on agricultural practices or other professions, means of livelihood adopted locally. Helps in categorizing various socio-economic practices and its stress on ecosystems in different settings.
d. Classification based on various types and subtypes of ecosystem.
2. After categorization of villages into various clusters, parameters, factors, and drivers to be studied in the field are determined and subsequent data is collected.
3. Scientific and empirical data, cluster-wise, village-wise, ecosystem-wise are to be collected from the field for a period of 2 years with the help of volunteers.
4. Scientific data, such as climate data, meteorological, and hydrological data for a period of past 40-50 years are to be collected from Governmental records and other portals.
Modeling:
The modeling task is the final stage in the research work (barring publication), It is an intense data analysis and processing session, in which various discerning parameters are analyzed with all available statistical tools to determine linkages between all parameters and arrive at mathematical function form. It is very important to drive all functions to represent various combinations of nexus between parameters.
Expected Outcome:
After all the parametric function is developed in all possible combinations, a model developed may provide a customizable solution for each locality with or without the need of any interventions, a solution with a high degree of acceptance, lessening the chances of conflict, and providing optimum quantification of funds or resources to be deployed. At the end of the research, the model could be hosted as a portal to provide services in the similar domain.
An Appeal
For conducting such a rigorous task over this large area, we do need help of people out there, help in form of suggestions, guidance and more importantly funding or sponsorship.
We urge the community out there, to kindly sponsor us. Help us, and win this conquest together!!
https://buy.stripe.com/6oE5kx6CG14AdDG8ww